基于伯克利cs61b的java数据结构笔记
ppt部分
java基础
类内static方法可以被类名调用,对象定义方法只有对象能调用
当类不独立时,嵌套类很有用,并且显然隶属于另一个类。
- 如果其他类不应该使用嵌套类,则将嵌套类设为私有类
接口
public interface List61B<Item> {
public void addFirst(Item x);
public void addLast(Item y);
public Item getFirst();
public Item getLast();
public Item removeLast();
public Item get(int i);
public void insert(Item x, int position);
public int size();
}
public static String longest(List61B<String> list) {
int maxDex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i += 1) {
String longestString = list.get(maxDex);
String thisString = list.get(i);
if (thisString.length() > longestString.length()) {
maxDex = i;
}
}
return list.get(maxDex);
} override重写:特征值不变,子类重写父类
overload重载:特征值改变
Java 有 8 种基本类型。 所有其他类型都是引用类型。
对于每个基本类型,都有一个相应的引用类型,称为
包装类。
- 例如,boolean的包装类是Boolean。
基本类型不能用在模板上,包装类可以
- 如果 Java 代码需要包装类型并获取原语,则会自动装箱。
- 如果代码需要一个原语并获得一个包装器,则它会被拆箱。
- 数组永远不会自动装箱/拆箱,例如 Integer[] 不能用于
int[] 的位置(反之亦然)。
- 自动装箱/拆箱会对性能产生可衡量的影响!
- 包装类型比原始类型使用更多的内存。
public final ArrayDeque<String> d = new ArrayDeque<String>();
- The d variable can never change, but the referenced deque can
Arrays are covariant:
- A FrenchDog is-a Dog.
- An FrenchDog[] is-a Dog[].
Generic types are invariant:
- A List<FrenchDog> is NOT a List<Dog>.
java实现链表
import java.util.Objects;
public class LinkedListDeque<T> {
public class Node {
Node next,prev=null;
T value;
public Node(T val) {
value=val;
}
public Node() {
}
}
int size=0;
Node firstnode = new Node();
public LinkedListDeque() {
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return Objects.equals(size,0);
}
public void addFirst(T item) {
Node new_node=new Node(item);
if (isEmpty()) {
firstnode.next=firstnode.prev=new_node;
new_node.next=new_node.prev=firstnode;
}
else {
firstnode.next.prev=new_node;
new_node.next=firstnode.next;
firstnode.next=new_node;
new_node.prev=firstnode;
}
size++;
}
public void addLast(T item) {
Node new_node=new Node(item);
if (isEmpty()) {
firstnode.next=firstnode.prev=new_node;
new_node.next=new_node.prev=firstnode;
}
else {
new_node.prev=firstnode.prev;
firstnode.prev.next=new_node;
firstnode.prev=new_node;
new_node.next=firstnode;
}
size++;
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
public void printDeque() {
Node temp=firstnode.next;
while (temp!= firstnode) {
System.out.println(temp.value);
temp=temp.next;
}
}
public T removeFirst() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
else if (size()==1) {
T val=firstnode.next.value;
firstnode.prev=firstnode.next=null;
size--;
return val;
}
else {
T val= firstnode.next.value;
firstnode.next.next.prev=firstnode;
firstnode.next=firstnode.next.next;
size--;
return val;
}
}
public T removeLast() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
else if (size()==1) {
T val;
val=firstnode.next.value;
firstnode.prev=firstnode.next=null;
size--;
return val;
}
else {
T val;
val=firstnode.prev.value;
firstnode.prev.prev.next=firstnode;
firstnode.prev=firstnode.prev.prev;
size--;
return val;
}
}
public T get(int index) {
if (index>size()-1) {
return null;
}
else {
Node temp = firstnode;
for (int i=0;i<index;i++) {
temp=temp.next;
}
return temp.value;
}
}
} java单元测试
@test
public void testMethod() {
assertEquals(<expected>, <actual>);
} 创建 JUnit 测试文件时,应在每个测试方法前面加上 @Test注解,并且可以有一个或多个 assertEquals或者 assertTrue方法(由 JUnit 库提供)。 所有测试必须是非静态的。 这可能看起来很奇怪,因为您的测试不使用实例变量并且您 可能不会实例化该类。 然而,设计师们却是这样的 JUnit 决定应该编写测试,所以我们就这么做。
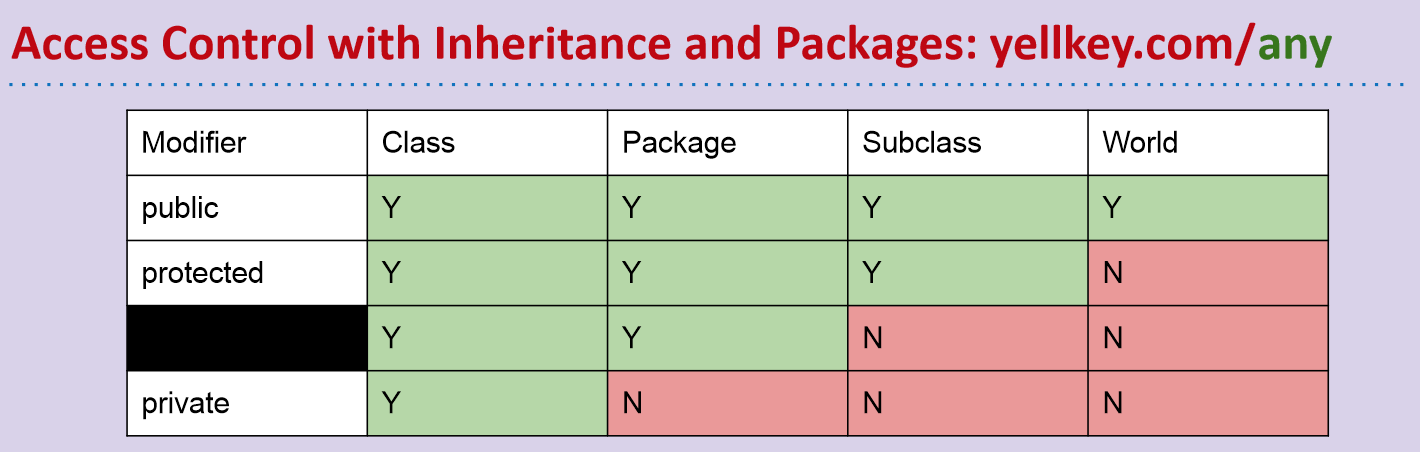
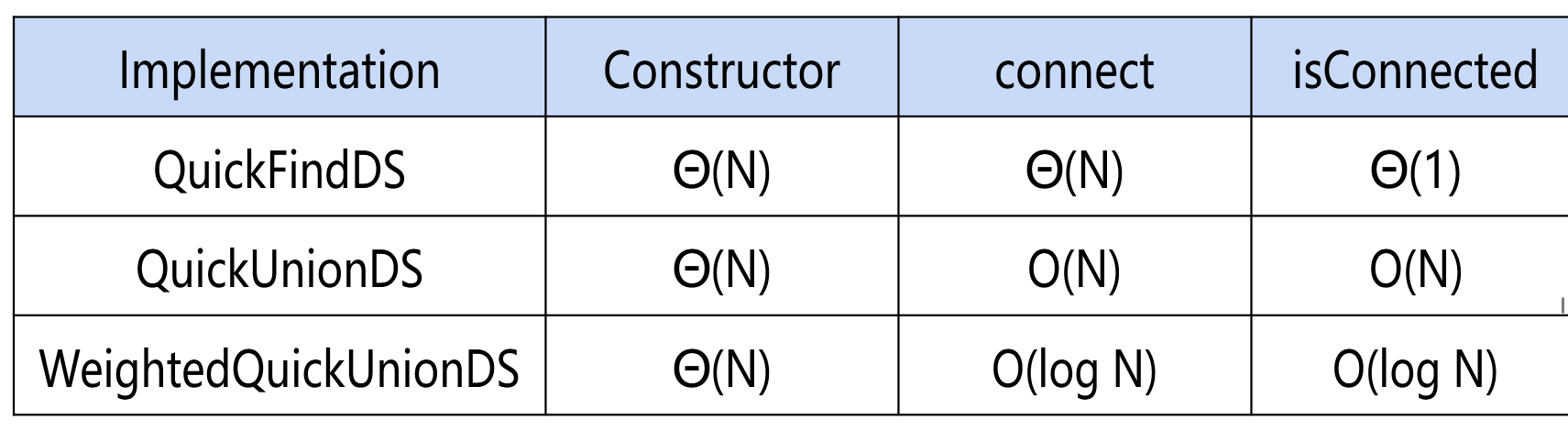
权限控制
BST IN JAVA

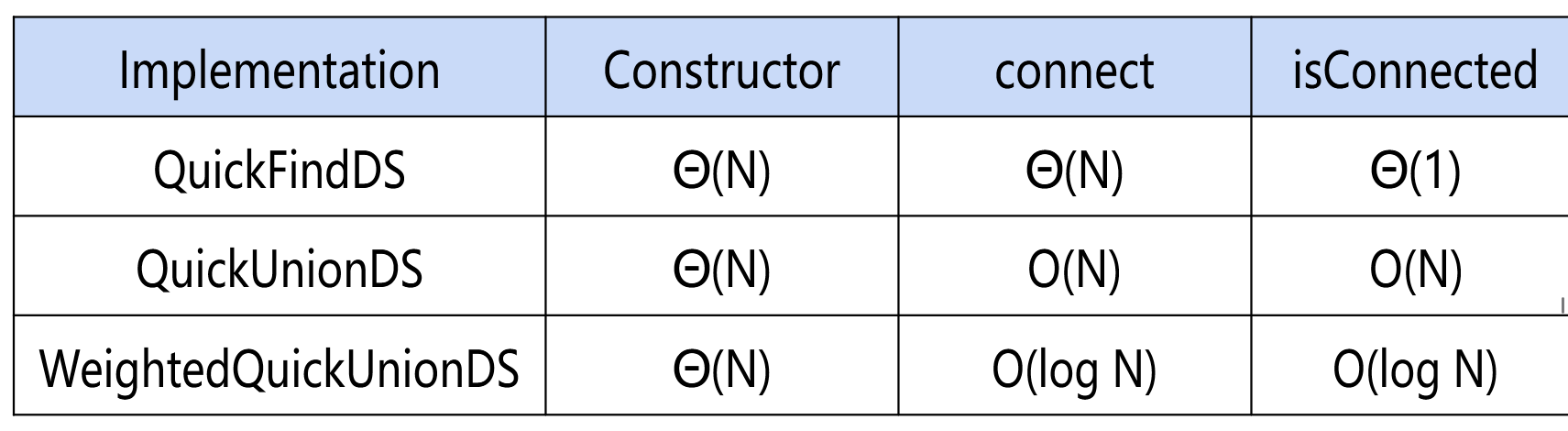
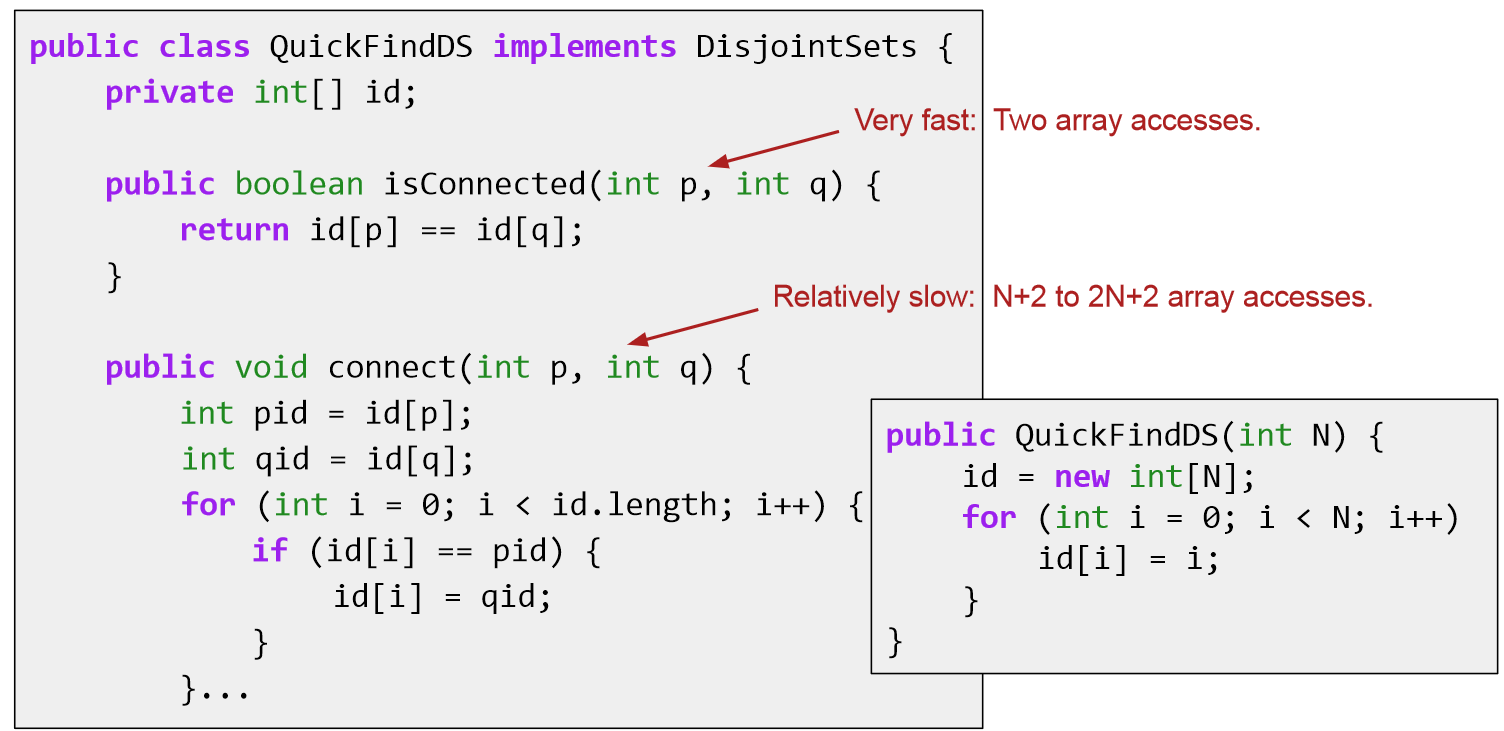
表示连接的数组:若数字相同则这些节点互相可达
增加父节点后形成bst
加权bst

维护一个size数组,只能将较小的树加到较大的树上
完整代码
public class WeightedQuickUnionDSWithPathCompression implements DisjointSets {
private int[] parent; private int[] size;
public WeightedQuickUnionDSWithPathCompression(int N) {
parent = new int[N]; size = new int[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
size[i] = 1;
}
}
private int find(int p) {
if (p == parent[p]) {
return p;
} else {
parent[p] = find(parent[p]);
return parent[p];
}
}
public boolean isConnected(int p, int q) {
return find(p) == find(q);
}
public void connect(int p, int q) {
int i = find(p);
int j = find(q);
if (i == j) return;
if (size[i] < size[j]) {
parent[i] = j; size[j] += size[i];
}
else {
parent[j] = i; size[i] += size[j];
}
} 树的旋转
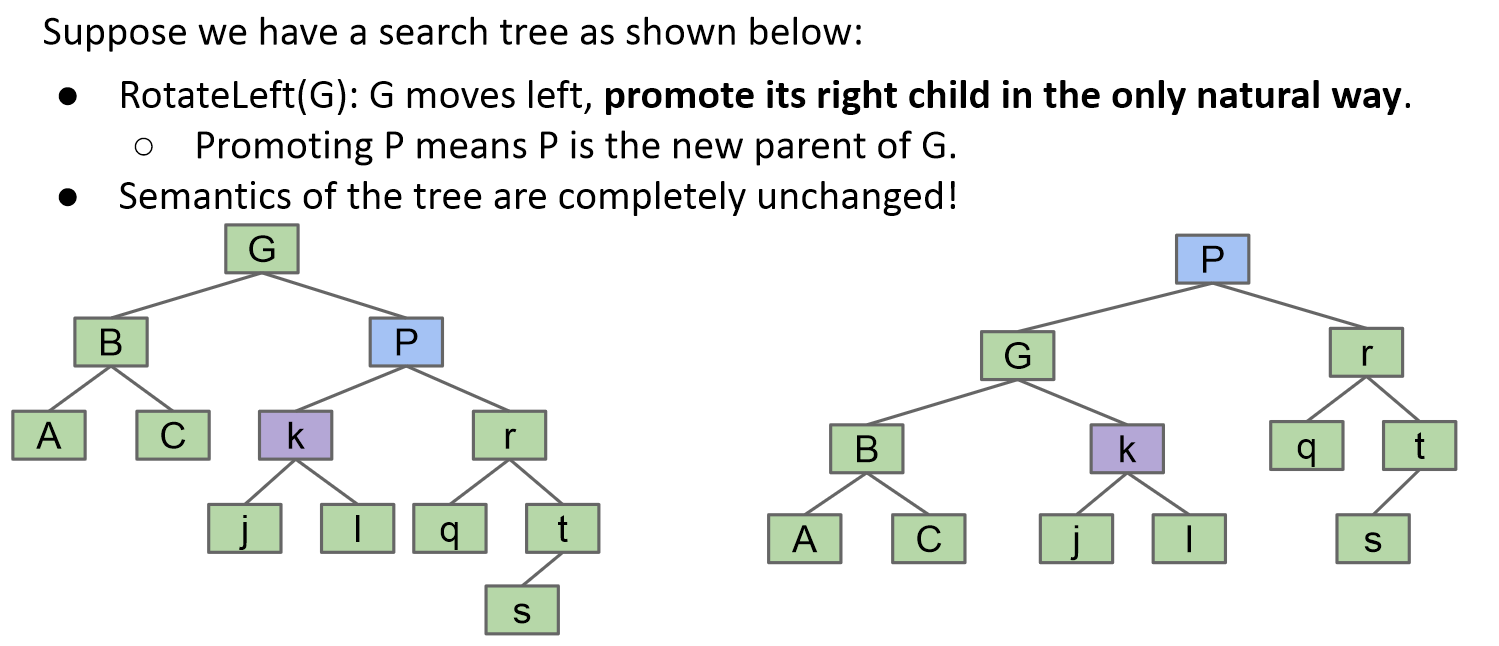
右旋同理
如果叶节点有最大负载限制
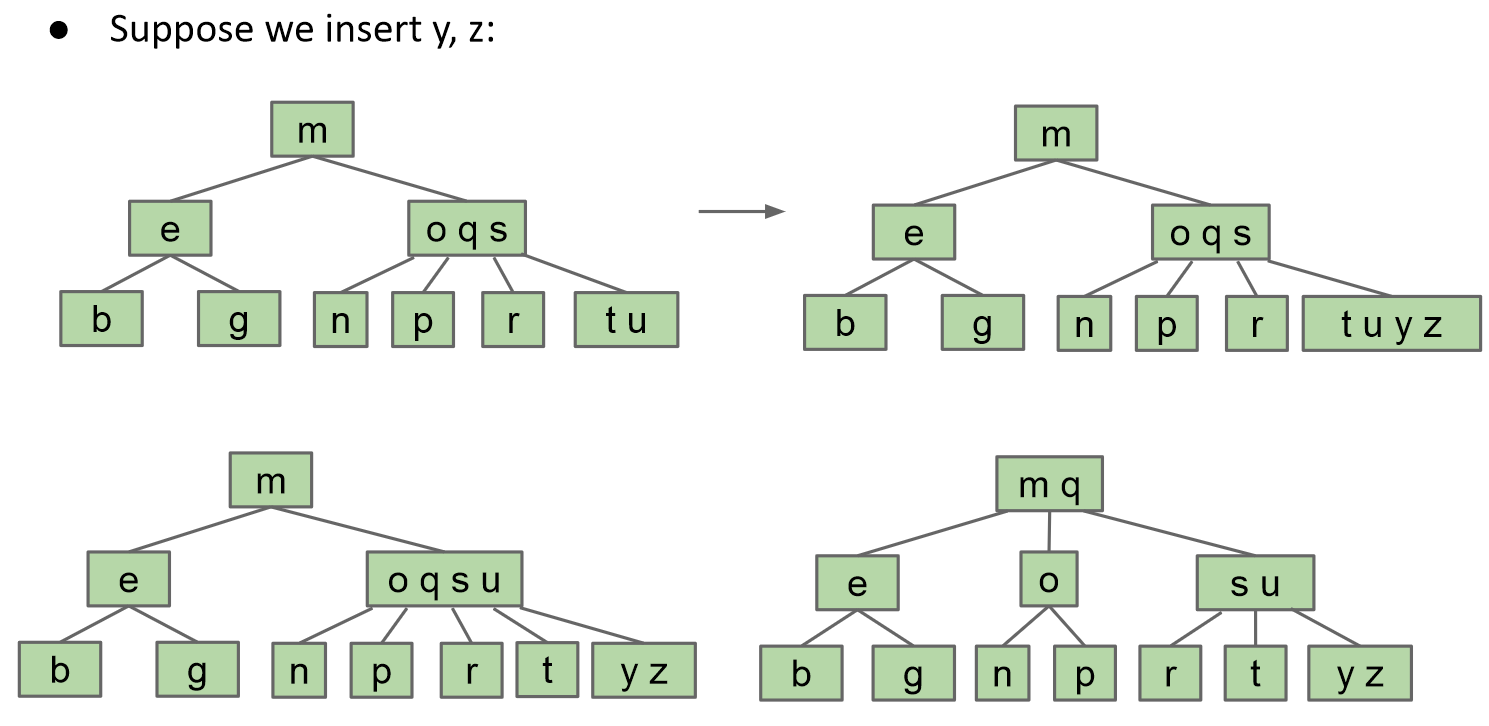
分裂树(B树)具有完美的平衡。
- 如果我们分裂根,每个节点都会被下推一层。
- 如果我们分割叶节点或内部节点,高度不会改变
所有操作Θ(log N)
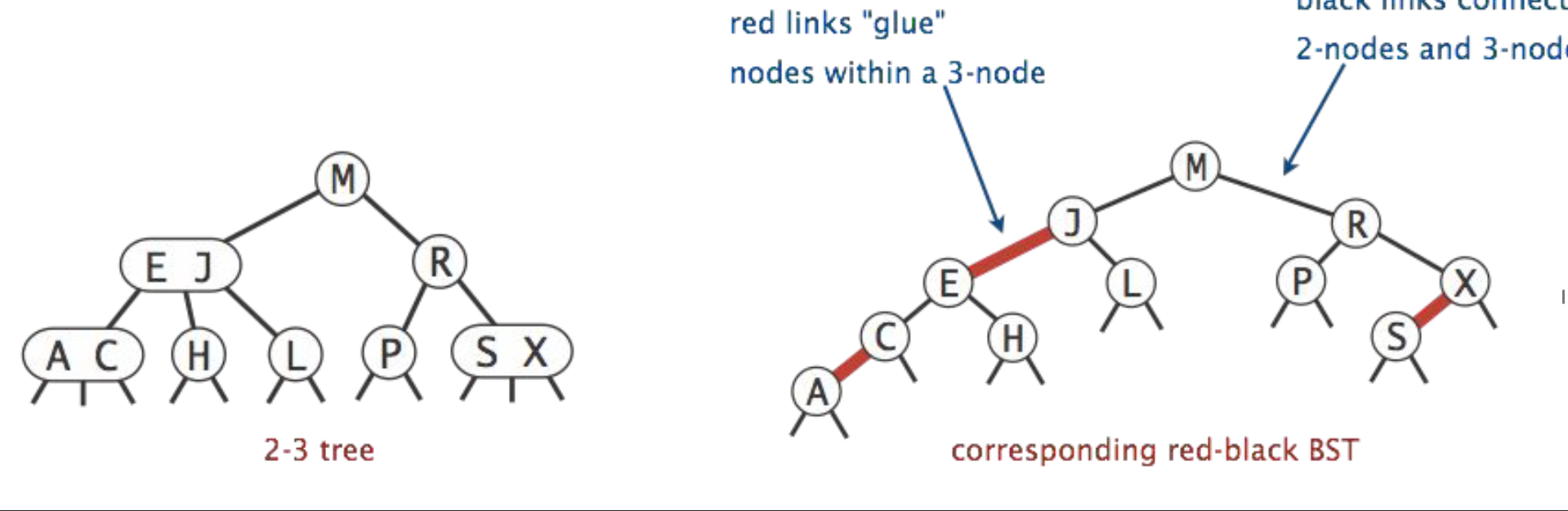
红黑树
任何与 2-3 树保持等距的 BST 都具有以下属性:
- 没有节点有两个红色链接(否则它就像一个 4 节点)。
- 从根到叶子的每条路径都有相同数量的黑色链接。
- 红色链接向左倾斜。
- 也称为“左倾红黑二叉搜索树(LLRB)
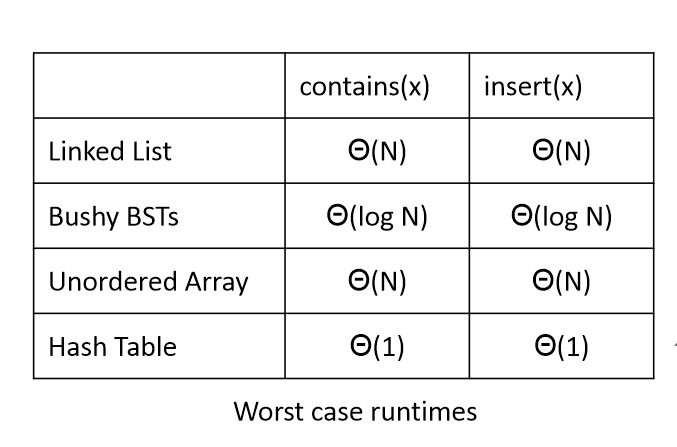
hash
如果 N 个项目分布在 M 个桶中,则平均时间取决于
N/M = L,也称为 负载系数 .
○ 平均运行时间为 Θ (L)。
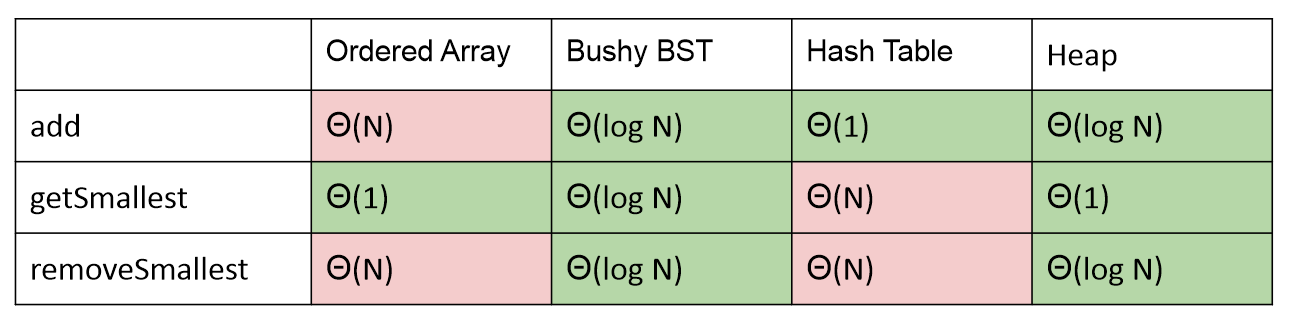
最小堆
二叉最小堆:二叉树完整,并服从 最小堆属性 .
- 最小堆:每个节点都小于或等于其两个子节点。
- 完整:仅在底层(如果有)缺少项目,所有节点都尽可能远
尽可能左。
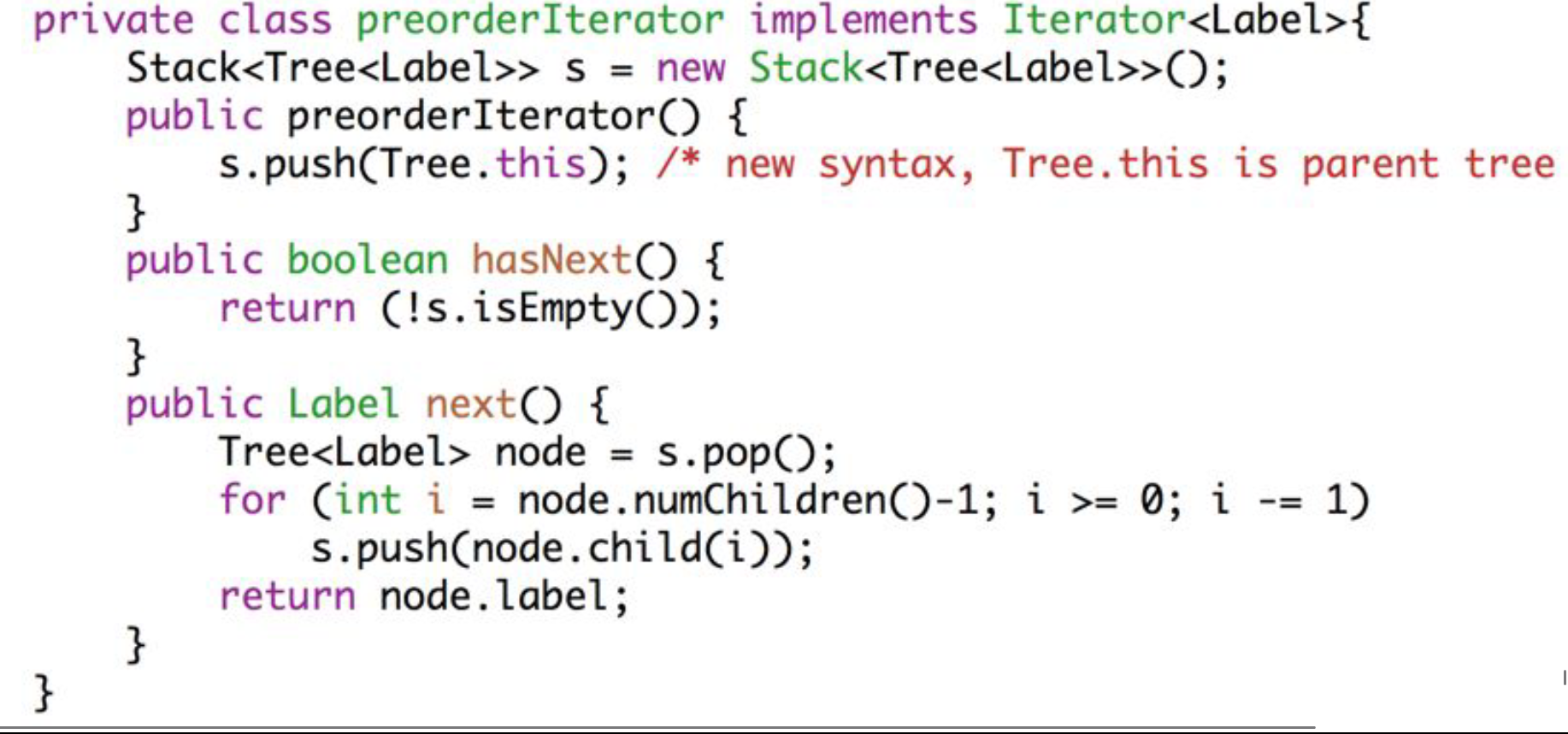
遍历
- 节点遍历:前中后序
- 层次遍历
实现指针接口——使用栈
两个类的equals实现,如果是哈希,一般需要同时确保hashcode方法对内容相同的类返回相同的哈希码
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o==this) return true;
if (o==null) return false;
if (o.getClass()!=this.getClass()) return false;
SimpleOomage new_o=(SimpleOomage) o;
return new_o.blue==this.blue &&new_o.red==this.red && new_o.green==this.green;
} 图论
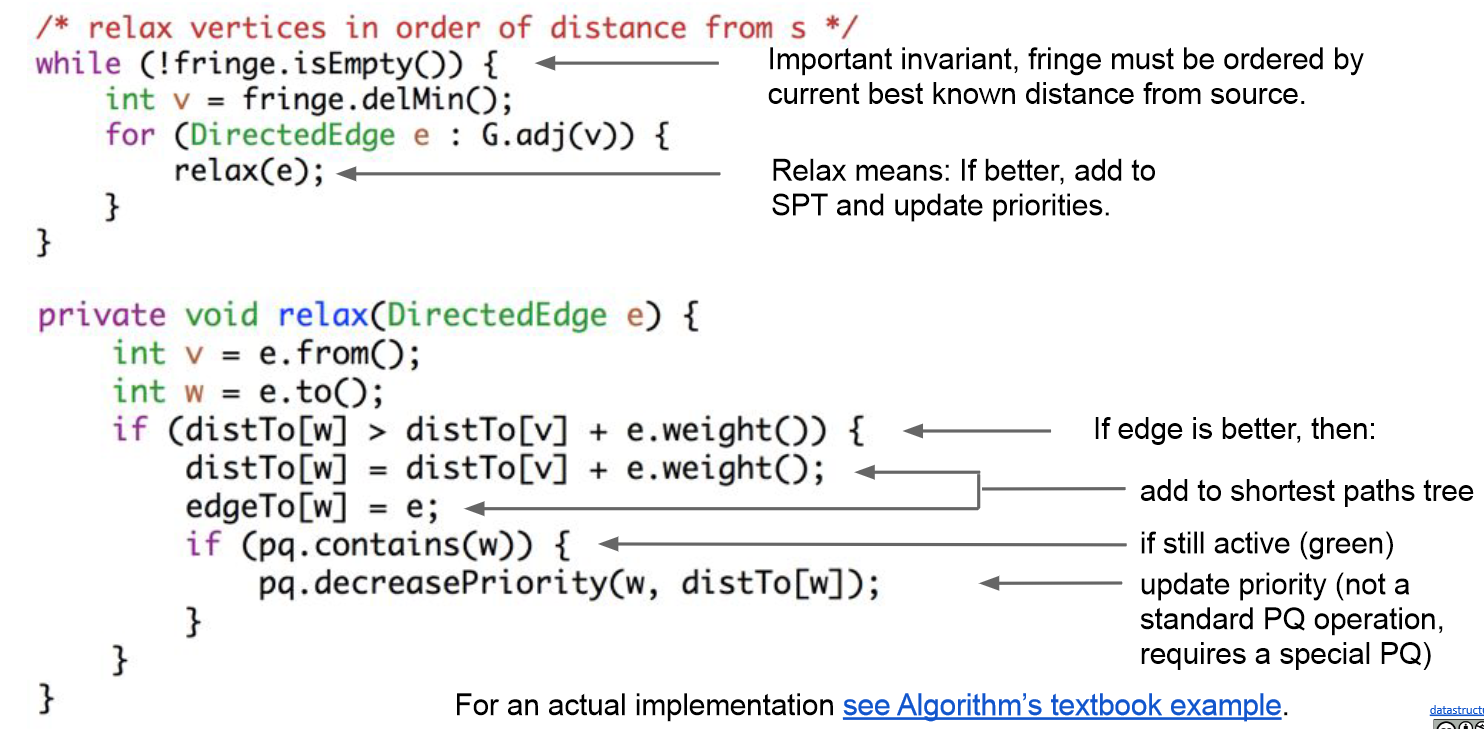
迪杰斯特拉
最小生成树(MST)
最短路径树取决于起始顶点:
- 因为它告诉你如何从源头到达一切。
MST 没有来源。
尽管如此,MST 有时恰好是特定顶点的 SPT
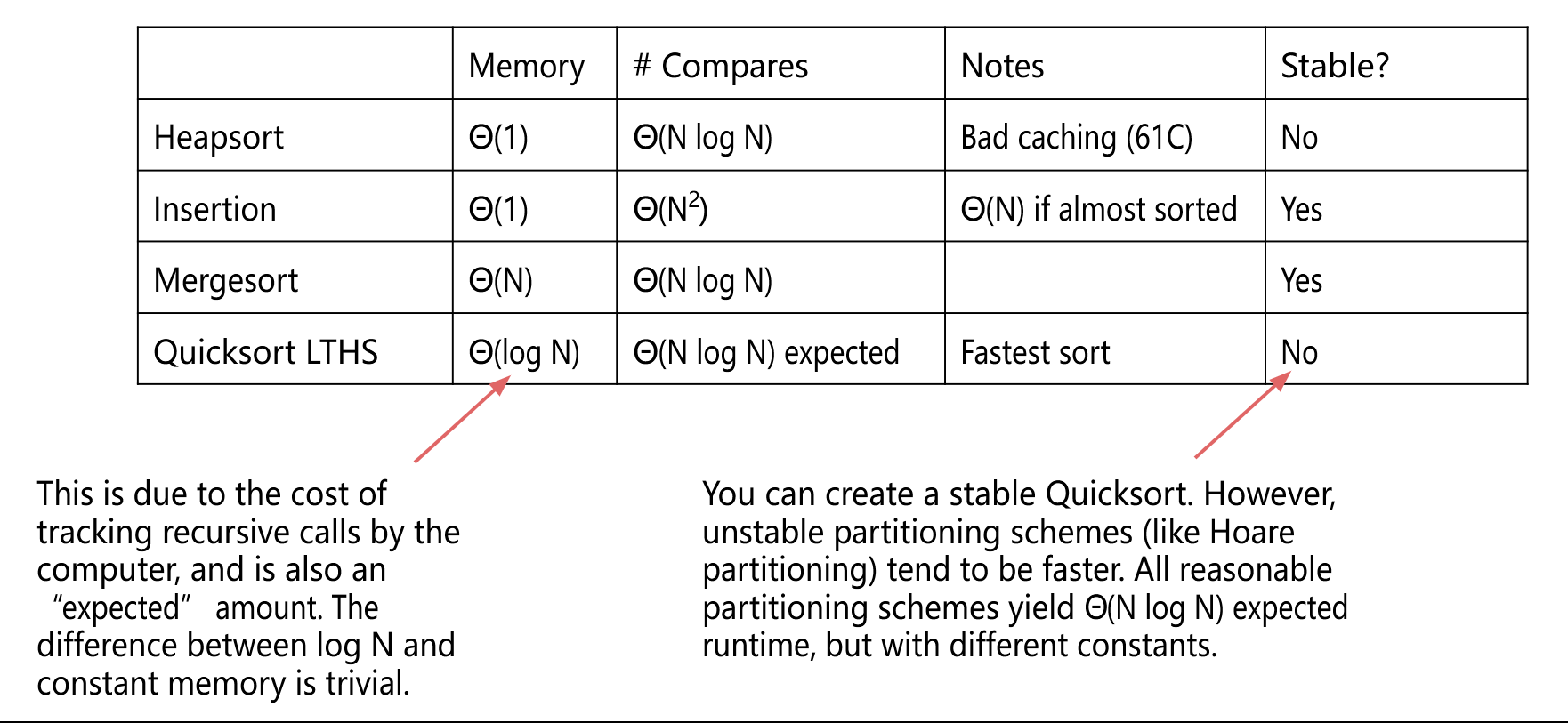
排序
稳定性:如果保留等价项的顺序,则称排序是稳定的。
- 选择排序:找到最小的项并将其放在前面。
- 插入排序:找出当前项插入的位置。
- 归并排序:将两个已排序的半部分合并为一个已排序的整体。
- 分区(快速)排序:围绕枢轴对项目进行分区。
快速排序
演示
不严谨地证明快排性能
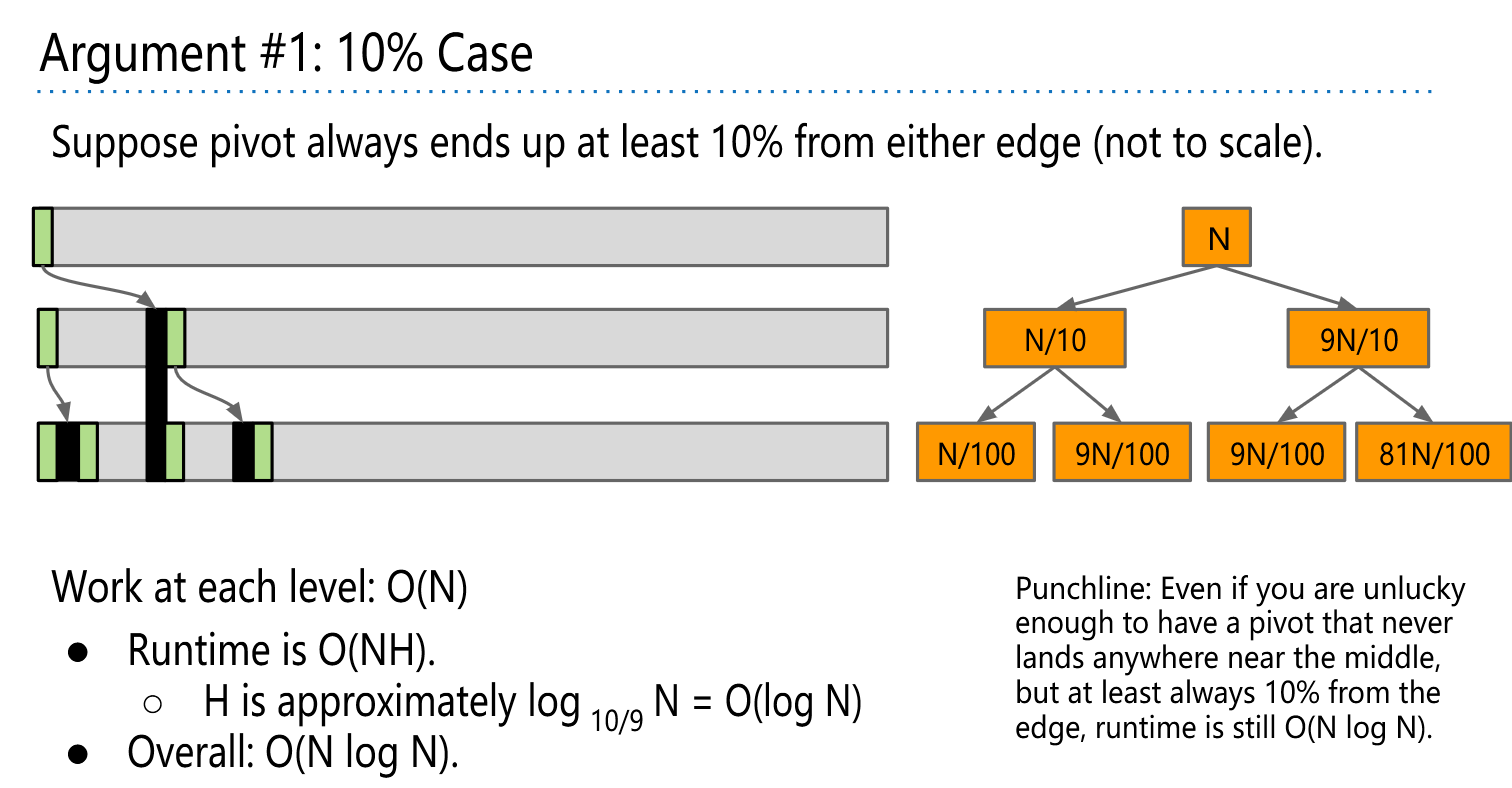
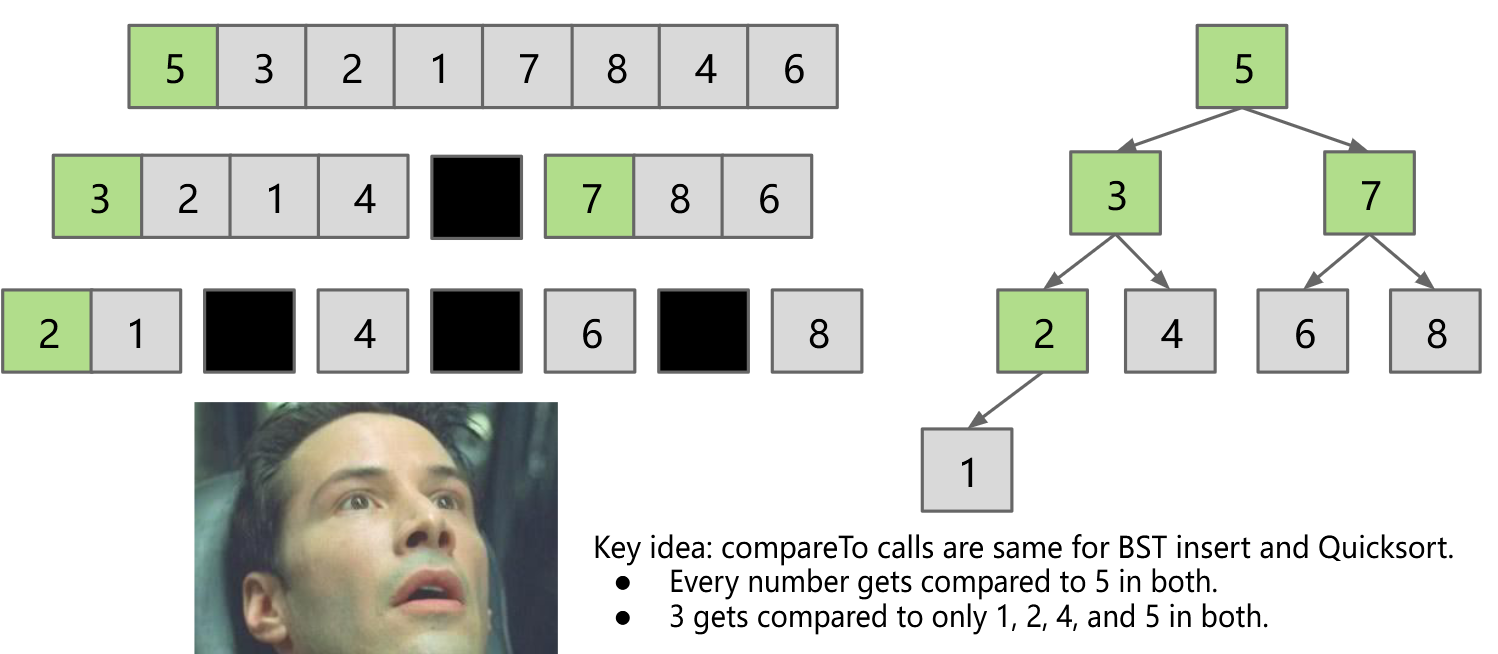
Quicksort is BST Sort
优化
- 切换到插入排序:- 当子问题大小减小到15或更小时,使用插入排序。
- 使排序自适应:利用数组中已有的顺序(插入排序,平滑排序,TimSort(Python和Java中的排序))。
- 利用键集的限制。如果键的个数是某个常数,例如[3, 4, 1, 2, 4, 3, ..., 2, 2, 2, 1, 4, 3, 2, 3],可以更快排序(参见三路快速排序,如果你好奇可以看这里:http://goo.gl/3sYnv3)。
- 对于快速排序:使算法具有自我检查能力,如果递归太深则切换到不同的排序方法。这只是确定性快速排序的问题。
在 Java 中,Arrays.sort(someArray) 使用:
- 合并排序(特别是 TimSort 变体)如果 someArray 包含
对象。
- 如果 someArray 由基本类型组成,则进行快速排序。
证明
- We have that N! > (N/2) N/2
- Taking the log of both sides, we have that log(N!) > log((N/2) N/2 ).
- Bringing down the exponent we have that log(N!) > N/2 log(N/2).
- Discarding the unnecessary constant, we have log(N!) ∈ Ω(N log (N/2)).
- From there, we have that log(N!) ∈ Ω(N log N).
- log(N!) = log(N) + log(N-1) + log(N-2) + …. + log(1)
- N log N = log(N) + log(N) + log(N) + … log(N)
- Therefore N log N ∈ Ω(log(N!))
结论:
N log N ∈ Θ(log N!)
log N! ∈ Θ(N log N) 比较排序中:
- Decision tree needs N! leaves.
- So we need lg(N!) rounded up levels, which is Ω(log(N!))
数据集
Digit-by-Digit
演示
Given a Trie with N keys, and a key with L digits. What is the:
- Worst case insert runtime? Θ(L)
- Worst case search runtime? Θ(L)
- Best case search runtime? Θ(1)
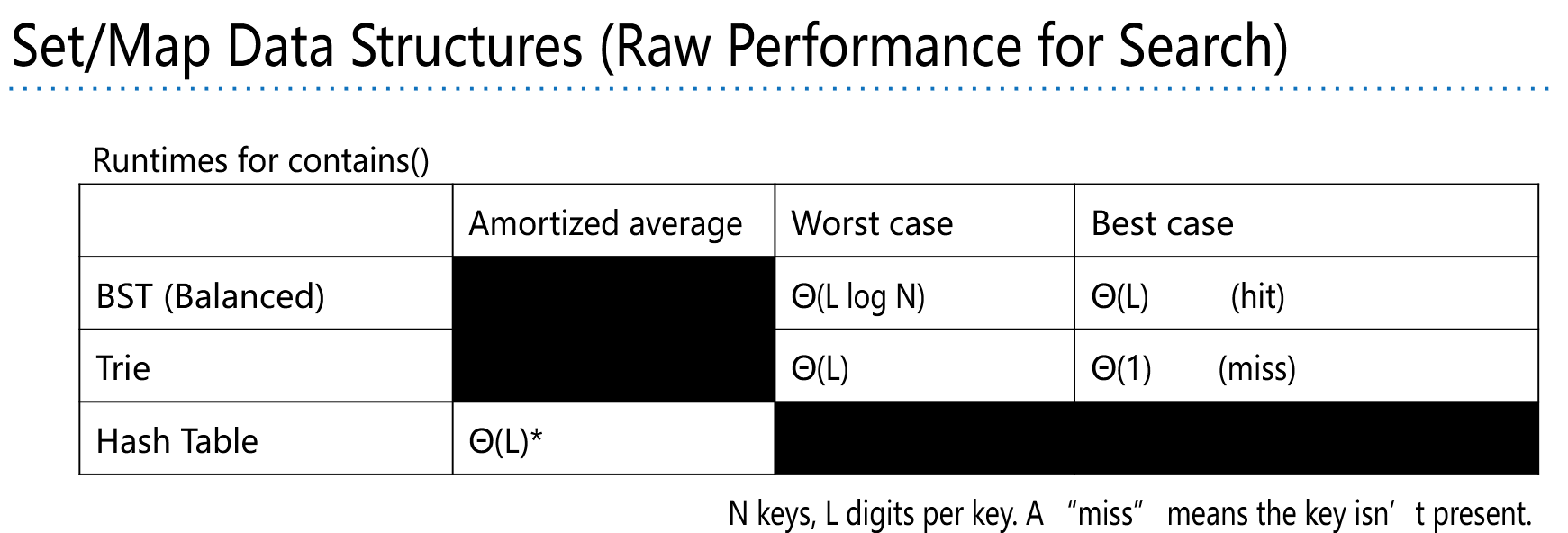

优化:
- Data-indexed array: Max speed, max memory.
- TreeMap/HashMap: Slower query performance, but less memory wasted.
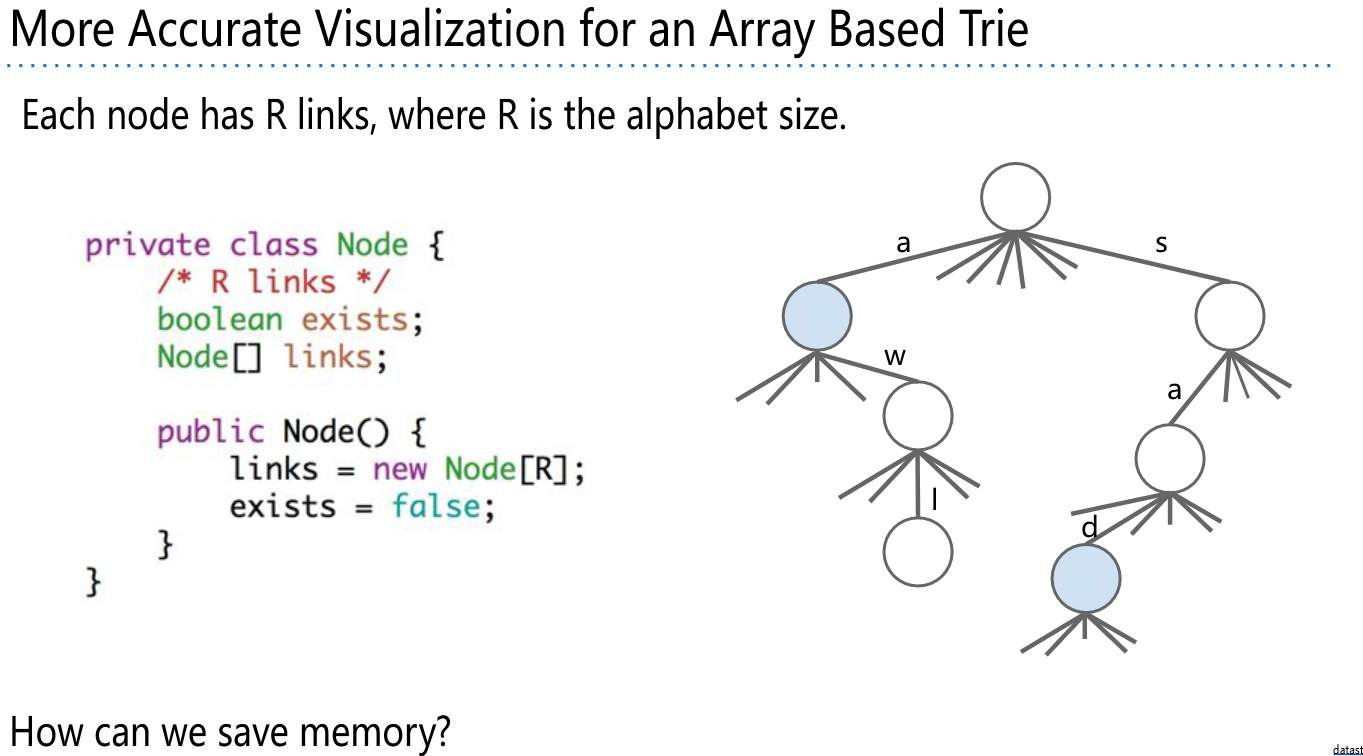

三元搜索
- 为每个节点分配一个字符。
- 给每个节点 3 个链接:
○ 如果键的下一个字符 < 节点的字符,则左链接。
○ 如果键的下一个字符 == 节点的字符,则中间链接。
○ 如果键的下一个字符 > 节点的字符,则右链接。
public class TST<Value> {
private int n; // size
private Node<Value> root; // root of TST
private static class Node<Value> {
private char c; // character
private Node<Value> left, mid, right; // left, middle, and right subtries
private Value val; // value associated with string
} | 数据结构 | 平均复杂度 | 最坏情况 | 最好情况 | 内存消耗 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 哈希表 | Θ(L)* | Θ(NL) | ||
| 二叉搜索树 | Θ(L log N) | Θ(1) | Θ(NL) | |
| Trie (数组) | Θ(L) | Θ(1) | Θ(NLR) | |
| Trie (哈希表) | Θ(L) | Θ(1) | Θ(NL) | |
| Trie (树) | Θ(L log R) | Θ(1) | Θ(NL) | |
| TST | Θ(NL) | Θ(1) | Θ(NL) |
N keys, L digits per key, R alphabet size. A miss means the key isn’t present.
编码和压缩
A prefix-free code is one in which no codeword is a prefix of any other. Example for
English:
| 字符 | 编码 |
|---|---|
| space | 111 |
| E | 010 |
| T | 1101 |
| A | 1011 |
| O | 1001 |
| I | 1000 |
I ATE: 100011110111101010
Shannon-Fano编码
- Count relative frequencies of all characters in a text.
- Split into ‘left’ and ‘right halves’ of roughly equal frequency.
○ Left half gets a leading zero. Right half gets a leading one.
○ Repeat.
Huffman编码
- Assign each symbol to a node with weight = relative frequency.
- Take the two smallest nodes and merge them into a super node with weight
equal to sum of weights.
- Repeat until everything is part of a tree.
- 将每个符号分配给一个节点,权重=相对频率。
- 取两个最小的节点,合并成一个带权重的超级节点
等于权重之和。
- 重复直到所有东西都是树的一部分。
霍夫曼压缩
使用霍夫曼压缩的两种可能的原理:
- 为每种输入类型构建一个语料库。
- 对于每个可能的输入文件,仅为该文件创建一个唯一的代码。 发送
代码与压缩文件一起。
实例:演示
编码:
第 1 步:计算频率。
步骤2:构建编码数组和解码树。
步骤3:将解码trie写入output.huf。
步骤4:将每个符号的码字写入output.huf。
解码:
步骤1:读入解码树。
步骤 2:沿着 trie 遍历,每次都输出符号 当到达一片叶子。
Given a file X.txt that we’d like to compress into X.huf:
- Consider each b-bit symbol (e.g. 8-bit chunks, Unicode characters, etc.) of
X.txt, counting occurrences of each of the 2 b possibilities, where b is the size
of each symbol in bits.
- Use Huffman code construction algorithm to create a decoding trie and
encoding map. Store this trie at the beginning of X.huf.
- Use encoding map to write codeword for each symbol of input into X.huf.
To decompress X.huf:
- Read in the decoding trie.
- Repeatedly use the decoding trie’s longestPrefixOf operation until all bits in
X.hug have been converted back to their uncompressed form. LZW压缩
演示
Key idea: Each codeword represents multiple symbols.
- Start with ‘trivial’ codeword table where each codeword corresponds to
one ASCII symbol.
- Every time a codeword X is used, record a new codeword Y corresponding
to X concatenated with the next symbol
- 从“简单”码字表开始,其中每个码字对应
一个 ASCII 符号。
- 每使用一个码字X,记录一个对应的新码字Y
到 X 与下一个符号连接。
总结
霍夫曼编码:
- 将公共符号表示为具有较少位的码字。
- 使用诸如 Map<Character, BitSeq> 之类的东西进行压缩。
- 使用 TrieMap<Character> 之类的东西进行解压缩。
LZW:
- 用单个码字表示多个符号。
- 使用 TrieMap<Integer> 之类的东西进行压缩。
- 使用诸如 Map<Character, SymbolSeq> 之类的东西进行解压缩。
附加内容
柯尔莫哥洛夫复杂度
Given a target bitstream B, what is the shortest bitstream C B that outputs B.
- Definition: The Java-Kolmogorov complexity K J (B) is the length of the
shortest Java program (in bytes) that generates B.
○ There IS an answer. It just might be very hard to find.
- 柯尔莫哥洛夫复杂度实际上与语言无关。
- 对于任何比特流,Java-Kolmogorov 复杂度不超过 大于 Python-Kolmogorov 复杂度的常数因子。—— I could just write a Python interpreter in Java and then run Kevin’s program.
○ K J (B) ≤ K P (B) + size(python interpreter)
- It is impossible to write a program that calculates the Kolmogorov
Complexity of any bitstream. Proof available here
独立集问题
独立集是一组顶点,其中没有两个顶点相邻。
独立集问题:
- 是否存在大小为 k 的独立集合?
- 即,k 个顶点的颜色为红色,这样就没有接触。
Give an algorithm for solving this problem.
- For each of the possible 2 N colorings:
○ Check if number of colored vertices is equal to k: O(N)
○ For every red vertex, check that neighbors are all white: O(k*N)
○ If both checks succeed, return true.
○ If either check fails, go on to next coloring.
- Runtime: O(k*N*2 N ). Since k ≤ N, O(N 2 *2 N ) np=p
We say that a problem is in the complexity class P if:
- It is a decision problem.
- An answer can be found in O(N k ) time for some k
We say that a problem is in the complexity class NP if:
- It is a decision problem.
- A “yes” answer can be verified in O(N k ) time for some k. More precisely, we
can verify a specific example of a “yes” answer in O(N k ) time
Many (most?) practical problems can be cast as a problem in NP:
- Is there a way to route my airplanes at a total cost of less than $1B/yr?
- Is there a way to route the wires inside this microchip with a total path
length of less than 1 micrometer?
- Given Z, are there two primes such that X*Y = Z?
- Is there a protein configuration for amino acid sequence X whose total
energy is less than Y?
Nice features of P:
- O(N k ) is closed under addition and multiplication.
○ Run two P algorithms, overall still in P.
○ Run a P algorithm in N times, still in P
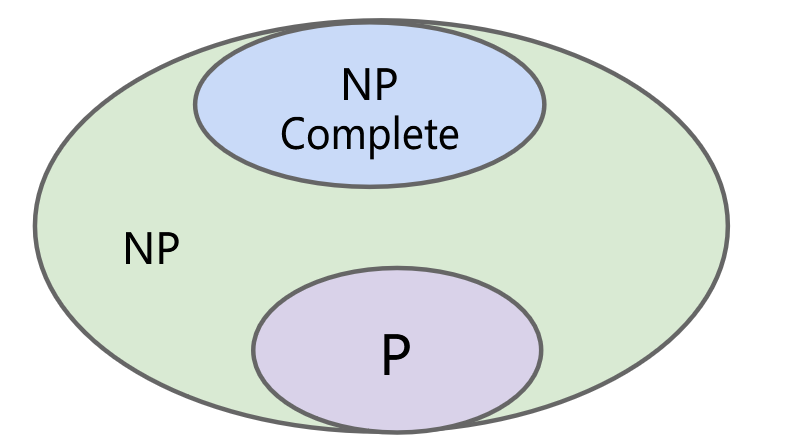
共识意见
- 83%:P ≠ NP(126 名受访者)
- 9%:P = NP(12 名受访者)
- 9%:其他(13 名受访者)
“[针对我们现在所说的 NP 完全问题的线性或二次时间过程将会产生]最严重的后果。[对于这样的程序]将 明确表明,尽管Entscheidungs问题无法解决,数学家在回答是或否问题时的脑力劳动可以是完全被机器取代了。” ——库尔特·哥德尔 总结
基于对象的编程:围绕对象进行组织。
面向对象编程:
○ 接口继承。
○ 实现继承。
动态类型与静态类型。
泛型编程,例如ArrayList<Integer>等。
内存模型是包含位的盒子。
正整数的位表示。
java
一些标准的编程习惯/模式:
○ 作为函数容器的对象(例如比较器、IntUnaryFunctions)。
○ 接口中的默认方法规范(链接)。
○ 迭代器和视图(例如keySet)。Java 中重要的数据结构
重要数据结构接口:
java.util.Collection(及其子类型)。
○ 特别强调 Map(及其子类型)。
我们自己的集合(例如Map61B、Deque):实际上并没有扩展集合。
运行时间分析
时间复杂度表示
渐进分析
数学证明
最好,最坏,平均情况数据结构
Array-Based Data Structures:
ArrayLists and ArrayDeque
HashSets, HashMaps, MyHashMap: Arrays of ‘buckets’
ArrayHeap (tree represented as an array)
Linked Data Structures
Linked Lists
○ LinkedList, IntList, LinkedListDeque, SLList, DLList
Trees: Hierarchical generalization of a linked list. Aim for bushiness.
○ TreeSet, TreeMap, BSTMap, Tries (trie links often stored as arrays)
Graphs: Generalization of a tree (including many algorithms).
编程实践
Java 语法和习惯用法。
JUnit 测试(及其更极端的形式:测试驱动开发)。
挖掘网络代码。
调试:
○ 确定受错误影响的最简单的情况。
○ 追捕它,让它无处藏身。
○ 有了正确的方法,即使通过查找bug也能找到bug
手动代码检查是不可能的(参见lab3中的Horrible Steve)。
真正的工具:IntelliJ、git、命令行、Maven
数据结构选择(和API设计)
○ 推动整个计划的绩效和实施。
使用复杂的 API、规范:项目 2 和项目 3
○ 项目 3 还涉及与现有代码库的交互。其他
压缩:霍夫曼编码,以及霍夫曼编码的数据结构选择。
其他方法:LZW 和游程编码(额外的幻灯片)。
观察:比特流的最佳压缩将提供 该位流的有用模型(例如,hugPlant.bmp -> HugPlant.java)。
不可能且棘手的问题:
不可能:为任何输入找到最佳压缩的算法。
棘手问题:3SAT、独立集、NP 完备性。
○ P = NP 吗? “是”的答案具有戏剧性的意义。
作业中的实现
BSTMap
remove思路:删除节点要把左子树最大值或者右子树最小值提上来,deletemin的代码为
private Node removeMin(K key, Node p) {
if (p.left == null) {
return p.right;
}
p.left = removeMin(key, p.left);
return p;
} package lab9;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.HashSet;
/**
* Implementation of interface Map61B with BST as core data structure. * * @author Your name here
*/public class BSTMap<K extends Comparable<K>, V> implements Map61B<K, V> {
private int size=0;
private class Node {
/* (K, V) pair stored in this Node. */
private K key;
private V value;
/* Children of this Node. */
private Node left;
private Node right;
private Node(K k, V v) {
key = k;
value = v;
left=right=null;
}
private boolean isEmpty() {
return !(left==null && right==null);
}
}
private Node root; /* Root node of the tree. */
/* Creates an empty BSTMap. */ public BSTMap() {
this.clear();
}
/* Removes all of the mappings from this map. */
@Override
public void clear() {
root = null;
size = 0;
}
/** Returns the value mapped to by KEY in the subtree rooted in P.
* or null if this map contains no mapping for the key. */ private V getHelper(K key, Node p) {
if (p==null) return null;
if (key.compareTo(p.key)==0) return p.value;
if (p.key.compareTo(key)>0) {
return getHelper(key,p.left);
}
else return getHelper(key,p.right);
}
/** Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, or null if this
* map contains no mapping for the key. */ @Override
public V get(K key) {
V val=getHelper(key,this.root);
return val;
}
/** Returns a BSTMap rooted in p with (KEY, VALUE) added as a key-value mapping.
* Or if p is null, it returns a one node BSTMap containing (KEY, VALUE). */ private Node putHelper(K key, V value, Node p) {
if (p==null) return new Node(key,value);
int compare=key.compareTo(p.key);
if (compare<0) p.left = putHelper(key,value,p.left);
else if (compare>0) p.right = putHelper(key,value,p.right);
else p.value=value;
return p;
}
/** Inserts the key KEY
* If it is already present, updates value to be VALUE. */ @Override
public void put(K key, V value) {
root = putHelper(key,value,this.root);
size++;
}
/* Returns the number of key-value mappings in this map. */
@Override
public int size() {
return size;
}
//////////////// EVERYTHING BELOW THIS LINE IS OPTIONAL ////////////////
/* Returns a Set view of the keys contained in this map. */ private void traverseAdd(Node p, Set<K> keys) {
if (p == null) {
return;
}
keys.add(p.key);
traverseAdd(p.left, keys);
traverseAdd(p.right, keys);
}
@Override
public Set<K> keySet() {
Set<K> keys = new HashSet<>() {
};
traverseAdd(root, keys);
return keys;
}
/** Removes KEY from the tree if present
* returns VALUE removed, * null on failed removal. */ @Override
public V remove(K key) {
V val = get(key);
if (val == null || key == null) return null;
remove_helper(root,key);
size--;
return val;
}
public Node remove_helper(Node x,K key) {
if (x == null) return null;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0) x.left = remove_helper(x.left, key);
else if (cmp > 0) x.right = remove_helper(x.right, key);
else {
if (x.right == null) return x.left;
if (x.left == null) return x.right;
Node t = left_max(x.left);
x.key=t.key;
x.value=t.value;
}
return x;
}
/** Removes the key-value entry for the specified key only if it is
* currently mapped to the specified value. Returns the VALUE removed, * null on failed removal. **/ public Node left_max(Node p) {
if (p==null) return null;
Node temp=p;
while (p.right!=null) {
temp=p;
p=p.right;
}
temp.right=null;
return p;
}
@Override
public V remove(K key, V value) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
@Override
public Iterator<K> iterator() {
return keySet().iterator();
}
private Node removeMin(K key, Node p) {
if (p.left == null) {
return p.right;
}
p.left = removeMin(key, p.left);
return p;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BSTMap<String, Integer> bstmap = new BSTMap<>();
bstmap.put("hello", 5);
bstmap.put("cat", 10);
bstmap.put("fish", 22);
bstmap.put("zebra", 90);
bstmap.remove("hello");
}
} hashmap
由于put操作不确保成功,需要用操作前后差值作为size变化量
int hashCode = hash(key);
size -= buckets[hashCode].size;
buckets[hashCode].put(key, value);
size += buckets[hashCode].size; package lab9;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* A hash table-backed Map implementation. Provides amortized constant time * access to elements via get(), remove(), and put() in the best case. * * @author Your name here
*/public class MyHashMap<K, V> implements Map61B<K, V> {
private static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 16;
private static int now_size=DEFAULT_SIZE;
private static final double MAX_LF = 0.75;
private ArrayMap<K, V>[] buckets;
private int size=0;
private int loadFactor() {
return size / buckets.length;
}
public MyHashMap() {
buckets = new ArrayMap[DEFAULT_SIZE];
this.clear();
}
public MyHashMap(int new_size) {
buckets = new ArrayMap[new_size];
this.clear();
}
/* Removes all of the mappings from this map. */
@Override
public void clear() {
this.size = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < this.buckets.length; i += 1) {
this.buckets[i] = new ArrayMap<>();
}
}
/** Computes the hash function of the given key. Consists of
* computing the hashcode, followed by modding by the number of buckets. * To handle negative numbers properly, uses floorMod instead of %. */ private int hash(K key) {
if (key == null) {
return 0;
}
int numBuckets = buckets.length;
return Math.floorMod(key.hashCode(), numBuckets);
}
/* Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, or null if this
* map contains no mapping for the key. */ @Override
public V get(K key) {
if (key==null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to get() is null");
return buckets[hash(key)].get(key);
}
/* Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map. */
@Override
public void put(K key, V value) {
int hashCode = hash(key);
size -= buckets[hashCode].size;
buckets[hashCode].put(key, value);
size += buckets[hashCode].size;
if (loadFactor()>MAX_LF) {
now_size*=2;
MyHashMap<K, V> newHashMap = new MyHashMap<>(now_size);
for (ArrayMap<K, V> bucket : buckets) {
for (K one_key : bucket) {
newHashMap.put(one_key, bucket.get(one_key));
}
}
this.buckets = newHashMap.buckets;
this.size = newHashMap.size;
}
}
/* Returns the number of key-value mappings in this map. */
@Override
public int size() {
return size;
}
//////////////// EVERYTHING BELOW THIS LINE IS OPTIONAL ////////////////
/* Returns a Set view of the keys contained in this map. */ @Override
public Set<K> keySet() {
Set<K> keys =new HashSet<>();
for (int i =0;i<buckets.length;i++) {
keys.addAll(buckets[i].keySet());
}
return keys;
}
/* Removes the mapping for the specified key from this map if exists.
* Not required for this lab. If you don't implement this, throw an * UnsupportedOperationException. */ @Override
public V remove(K key) {
if (buckets[hash(key)].containsKey(key)) {
V val = buckets[hash(key)].get(key);
buckets[hash(key)].remove(key);
size--;
return val;
}
else return null;
}
/* Removes the entry for the specified key only if it is currently mapped to
* the specified value. Not required for this lab. If you don't implement this, * throw an UnsupportedOperationException.*/ @Override
public V remove(K key, V value) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
@Override
public Iterator<K> iterator() {
return keySet().iterator();
}
} 拓扑排序
public class DepthFirstOrder {
private boolean[] marked;
private Stack<Integer> reversePostorder;
public DepthFirstOrder(Digraph G) {
reversePostorder = new Stack<Integer>();
marked = new boolean[G.V()];
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) {
if (!marked[v]) { dfs(G, v); }
}
private void dfs(Digraph G, int v) {
marked[v] = true;
for (int w : G.adj(v)) {
if (!marked[w]) { dfs(G, w); }
}
reversePostorder.push(v);
}
public Iterable<Integer> reversePostorder()
{ return reversePostorder; }
最小堆
public class ArrayHeap<T> implements ExtrinsicPQ<T> {
private Node[] contents;
private int size;
public ArrayHeap() {
contents = new ArrayHeap.Node[16];
/* Add a dummy item at the front of the ArrayHeap so that the getLeft,
* getRight, and parent methods are nicer. */ contents[0] = null;
/* Even though there is an empty spot at the front, we still consider
* the size to be 0 since nothing has been inserted yet. */ size = 0;
}
/**
* Returns the index of the node to the left of the node at i. */ private static int leftIndex(int i) {
/* TODO: Your code here! */
return i*2;
}
/**
* Returns the index of the node to the right of the node at i. */ private static int rightIndex(int i) {
/* TODO: Your code here! */
return i*2+1;
}
/**
* Returns the index of the node that is the parent of the node at i. */ private static int parentIndex(int i) {
/* TODO: Your code here! */
return (int) i/2;
}
/**
* Gets the node at the ith index, or returns null if the index is out of * bounds. */ private Node getNode(int index) {
if (!inBounds(index)) {
return null;
}
return contents[index];
}
/**
* Returns true if the index corresponds to a valid item. For example, if * we have 5 items, then the valid indices are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5. Index 0 is * invalid because we leave the 0th entry blank. */ private boolean inBounds(int index) {
if ((index > size) || (index < 1)) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* Swap the nodes at the two indices. */ private void swap(int index1, int index2) {
Node node1 = getNode(index1);
Node node2 = getNode(index2);
contents[index1] = node2;
contents[index2] = node1;
}
/**
* Returns the index of the node with smaller priority. Precondition: not * both nodes are null. */ private int min(int index1, int index2) {
Node node1 = getNode(index1);
Node node2 = getNode(index2);
if (node1 == null) {
return index2;
} else if (node2 == null) {
return index1;
} else if (node1.myPriority < node2.myPriority) {
return index1;
} else {
return index2;
}
}
/**
* Bubbles up the node currently at the given index. */ private void swim(int index) {
// Throws an exception if index is invalid. DON'T CHANGE THIS LINE.
validateSinkSwimArg(index);
/** TODO: Your code here. */
while (index!=1 && min(index,parentIndex(index))==index) {
swap(index,parentIndex(index));
index=parentIndex(index);
}
}
/**
* Bubbles down the node currently at the given index. */ private void sink(int index) {
// Throws an exception if index is invalid. DON'T CHANGE THIS LINE.
validateSinkSwimArg(index);
/** TODO: Your code here. */
if (inBounds(rightIndex(index))) {
int min_index=min(leftIndex(index),rightIndex(index));
if (min(index,min_index)==min_index) {
swap(index,min_index);
sink(min_index);
}
} else if (inBounds(leftIndex(index))) {
int min_index = leftIndex(index);
if (min(index,min_index)==min_index) {
swap(index,min_index);
sink(min_index);
}
}
}
/**
* Inserts an item with the given priority value. This is enqueue, or offer. * To implement this method, add it to the end of the ArrayList, then swim it. */ @Override
public void insert(T item, double priority) {
/* If the array is totally full, resize. */
if (size + 1 == contents.length) {
resize(contents.length * 2);
}
/* TODO: Your code here! */
contents[size+1]=new Node(item,priority);
size++;
swim(size);
}
/**
* Returns the Node with the smallest priority value, but does not remove it * from the heap. To implement this, return the item in the 1st position of the ArrayList. */ @Override
public T peek() {
/* TODO: Your code here! */
return contents[1].myItem;
}
/**
* Returns the Node with the smallest priority value, and removes it from * the heap. This is dequeue, or poll. To implement this, swap the last * item from the heap into the root position, then sink the root. This is * equivalent to firing the president of the company, taking the last * person on the list on payroll, making them president, and then demoting * them repeatedly. Make sure to avoid loitering by nulling out the dead * item. */ @Override
public T removeMin() {
/* TODO: Your code here! */
T val=peek();
swap(1,size);
contents[size]=null;
size--;
sink(1);
return val;
}
/**
* Returns the number of items in the PQ. This is one less than the size * of the backing ArrayList because we leave the 0th element empty. This * method has been implemented for you. */ @Override
public int size() {
return size;
}
/**
* Change the node in this heap with the given item to have the given * priority. You can assume the heap will not have two nodes with the same * item. Check item equality with .equals(), not ==. This is a challenging * bonus problem, but shouldn't be too hard if you really understand heaps * and think about the algorithm before you start to code. */ @Override
public void changePriority(T item, double priority) {
/* TODO: Your code here! */
changePriority_helper(item,priority,1);
}
public void changePriority_helper(T item, double priority,int index) {
if (!inBounds(index)) return;
if (contents[index].myItem.equals(item)) contents[index].myPriority=priority;
else{
changePriority_helper(item, priority,leftIndex(index));
changePriority_helper(item,priority,rightIndex(index));
}
}
/**
* Prints out the heap sideways. Provided for you. */ @Override
public String toString() {
return toStringHelper(1, "");
}
/* Recursive helper method for toString. */
private String toStringHelper(int index, String soFar) {
if (getNode(index) == null) {
return "";
} else {
String toReturn = "";
int rightChild = rightIndex(index);
toReturn += toStringHelper(rightChild, " " + soFar);
if (getNode(rightChild) != null) {
toReturn += soFar + " /";
}
toReturn += "\n" + soFar + getNode(index) + "\n";
int leftChild = leftIndex(index);
if (getNode(leftChild) != null) {
toReturn += soFar + " \\";
}
toReturn += toStringHelper(leftChild, " " + soFar);
return toReturn;
}
}
/**
* Throws an exception if the index is invalid for sinking or swimming. */ private void validateSinkSwimArg(int index) {
if (index < 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot sink or swim nodes with index 0 or less");
}
if (index > size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot sink or swim nodes with index greater than current size.");
}
if (contents[index] == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot sink or swim a null node.");
}
}
private class Node {
private T myItem;
private double myPriority;
private Node(T item, double priority) {
myItem = item;
myPriority = priority;
}
public T item(){
return myItem;
}
public double priority() {
return myPriority;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return myItem.toString() + ", " + myPriority;
}
}
/** Helper function to resize the backing array when necessary. */
private void resize(int capacity) {
Node[] temp = new ArrayHeap.Node[capacity];
for (int i = 1; i < this.contents.length; i++) {
temp[i] = this.contents[i];
}
this.contents = temp;
}
最佳优先搜索BMS
从概念上讲,这个想法非常简单:
- 保留“移动序列”的优先级队列。
- 从 PQ 中删除“最佳”移动序列,我们称之为 BMS。
- 令 F 为 BMS 中的最后一个状态。
- 如果 F 是目标状态,则完成,因此返回 BMS。
- 如果F不是目标,则对于F的每个邻居N,创建一个由BMS + N组成的新移动序列并将其放入PQ中。
该算法也称为 A*搜索算法
public class Solver {
int times = 0;
SearchNode final_node;
private class SearchNode implements Comparable<SearchNode> {
private WorldState now_state;
private int mov_times = 0;
private SearchNode ref_state;
public SearchNode(WorldState ws,int times,SearchNode ref) {
this.now_state=ws;
this.mov_times=times;
this.ref_state=ref;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(SearchNode o) {
return this.mov_times+now_state.estimatedDistanceToGoal()-o.mov_times-o.now_state.estimatedDistanceToGoal();
}
}
public Solver(WorldState initial) {
MinPQ<SearchNode> pq = new MinPQ<>();
pq.insert(new SearchNode(initial,0,null));
while (true) {
SearchNode a_node = pq.delMin();
if (a_node.now_state.isGoal()) {
final_node=a_node;
break;
}
for (WorldState nb : a_node.now_state.neighbors()) {
if (a_node.ref_state == null || !nb.equals(a_node.ref_state.now_state)) pq.insert(new SearchNode(nb, a_node.mov_times + 1, a_node));
}
}
}
public int moves() {
return final_node.mov_times;
}
public Iterable<WorldState> solution() {
int movTimes = final_node.mov_times;
List<WorldState> ret = new ArrayList<>();
SearchNode temp= final_node;
ret.add(final_node.now_state);
while (temp.ref_state != null) {
ret.add(temp.ref_state.now_state);
temp=temp.ref_state;
}
return ret;
}
} 深度和广度优先搜索
public MazeDepthFirstPaths(Maze m, int sourceX, int sourceY, int targetX, int targetY) {
super(m);
maze = m;
s = maze.xyTo1D(sourceX, sourceY);
t = maze.xyTo1D(targetX, targetY);
distTo[s] = 0;
edgeTo[s] = s;
}
private void dfs(int v) {
marked[v] = true;
announce();
if (v == t) {
targetFound = true;
}
if (targetFound) {
return;
}
for (int w : maze.adj(v)) {
if (!marked[w]) {
edgeTo[w] = v;
announce();
distTo[w] = distTo[v] + 1;
dfs(w);
if (targetFound) {
return;
}
}
}
}
private void bfs() {
// TODO: Your code here. Don't forget to update distTo, edgeTo, and marked, as well as call announce()
ArrayDeque<Integer> q = new ArrayDeque<Integer>(maze.V());
for (int v = 0; v < maze.V(); v++) {
distTo[v] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
distTo[s] = 0;
marked[s] = true;
announce();
q.add(s);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int v = q.remove();
for (int w : maze.adj(v)) {
if (!marked[w]) {
edgeTo[w] = v;
distTo[w] = distTo[v] + 1;
marked[w] = true;
announce();
q.add(w);
}
}
}
} 归并排序
private static <Item extends Comparable> Item getMin(
Queue<Item> q1, Queue<Item> q2) {
if (q1.isEmpty()) {
return q2.dequeue();
} else if (q2.isEmpty()) {
return q1.dequeue();
} else {
// Peek at the minimum item in each queue (which will be at the front, since the
// queues are sorted) to determine which is smaller. Comparable q1Min = q1.peek();
Comparable q2Min = q2.peek();
if (q1Min.compareTo(q2Min) <= 0) {
// Make sure to call dequeue, so that the minimum item gets removed.
return q1.dequeue();
} else {
return q2.dequeue();
}
}
}
/** Returns a queue of queues that each contain one item from items. */
private static <Item extends Comparable> Queue<Queue<Item>>
makeSingleItemQueues(Queue<Item> items) {
// Your code here!
Queue<Queue<Item>> qq = new Queue<>();
for (Item it:items) {
Queue<Item> qe= new Queue<>();
qe.enqueue(it);
qq.enqueue(qe);
}
return qq;
}
/**
* Returns a new queue that contains the items in q1 and q2 in sorted order. * * This method should take time linear in the total number of items in q1 and q2. After * running this method, q1 and q2 will be empty, and all of their items will be in the * returned queue. * * @param q1 A Queue in sorted order from least to greatest.
* @param q2 A Queue in sorted order from least to greatest.
* @return A Queue containing all of the q1 and q2 in sorted order, from least to
* greatest. * */private static <Item extends Comparable> Queue<Item> mergeSortedQueues(
Queue<Item> q1, Queue<Item> q2) {
// Your code here!
Queue<Item> qi = new Queue<>();
while (!q1.isEmpty() || !q2.isEmpty()) {
qi.enqueue(getMin(q1,q2));
}
return qi;
}
/** Returns a Queue that contains the given items sorted from least to greatest. */
public static <Item extends Comparable> Queue<Item> mergeSort(
Queue<Item> items) {
// Your code here!
if (items.size()==1) return items;
Queue<Queue<Item>> temp = makeSingleItemQueues(items);
while (temp.size() > 1) {
Queue<Item> lft = temp.dequeue();
Queue<Item> rht = temp.dequeue();
Queue<Item> q = mergeSortedQueues(lft,rht);
temp.enqueue(q);
}
return temp.dequeue();
} 三元快速排序
private static <Item extends Comparable> void partition(
Queue<Item> unsorted, Item pivot,
Queue<Item> less, Queue<Item> equal, Queue<Item> greater) {
// Your code here!
while (!unsorted.isEmpty()) {
Item it = unsorted.dequeue();
if (it.compareTo(pivot)< 0) less.enqueue(it);
else if (it.compareTo(pivot)==0) equal.enqueue(it);
else greater.enqueue(it);
}
}
/** Returns a Queue that contains the given items sorted from least to greatest. */
public static <Item extends Comparable> Queue<Item> quickSort(
Queue<Item> items) {
// Your code here!
Item piv = getRandomItem(items);
Queue<Item> less = new Queue<>();
Queue<Item> equal = new Queue<>();
Queue<Item> greater = new Queue<>();
partition(items,piv,less,equal,greater);
if (!less.isEmpty()) less = quickSort(less);
if (!greater.isEmpty()) greater=quickSort(greater);
return catenate(catenate(less,equal),greater);
} 计数排序
public static int[] betterCountingSort(int[] arr) {
// TODO make counting sort work with arrays containing negative numbers.
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int neg = 0;
for (int i : arr) {
if (i<0) neg++;
max = Math.max(max, i);
min = Math.min(min, i);
}
int[] posicounts = new int[max + 1];
if (min < 0) {
int[] negacounts = new int[-min + 1];
for (int i : arr) {
if (i >= 0) posicounts[i]++;
else negacounts[-i]++;
}
int[] negsorted = new int[neg];
int k = 0;
for (int i = -min ; i >0 ; i -= 1) {
for (int j = 0; j < negacounts[i]; j += 1, k += 1) {
negsorted[k] = -i;
}
}
k=0;
int[] posisorted = new int[arr.length - neg];
for (int i = 0; i < posicounts.length; i += 1) {
for (int j = 0; j < posicounts[i]; j += 1, k += 1) {
posisorted[k] = i;
}
}
int[] result = Arrays.copyOf(negsorted, posisorted.length + negsorted.length);
System.arraycopy(posisorted, 0, result, posisorted.length, negsorted.length);
return result;
}
else {
for (int i: arr) {
posicounts[i]++;
}
int[] sorted = new int[arr.length];
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < posicounts.length; i += 1) {
for (int j = 0; j < posicounts[i]; j += 1, k += 1) {
sorted[k] = i;
}
}
return sorted;
}
}
} 另一种实现
public static int[] betterCountingSort(int[] arr) {
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i : arr) {
max = max > i ? max : i;
min = min < i ? min : i;
}
int[] counts = new int[max - min + 1];
for (int i : arr) {
counts[i - min]++;
}
int[] starts = new int[max - min + 1];
int pos = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < starts.length; i += 1) {
starts[i] = pos;
pos += counts[i];
}
int[] sorted = new int[arr.length];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i += 1) {
int item = arr[i];
int place = starts[item - min];
sorted[place] = item;
starts[item - min] += 1;
}
return sorted;
} 基数排序lsd
public static String[] sort(String[] asciis) {
// TODO: Implement LSD Sort
String[] result = new String[asciis.length];
String[] temp = asciis.clone();
int max =Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (String str:asciis) {
if (max < str.length()) max = str.length();
}
for (int i = max-1; i >=0; i--) {
temp = sortHelperLSD(temp, i);
}
return temp;
}
/**
* LSD helper method that performs a destructive counting sort the array of * Strings based off characters at a specific index. * @param asciis Input array of Strings
* @param index The position to sort the Strings on.
*/private static String[] sortHelperLSD(String[] asciis, int index) {
// Optional LSD helper method for required LSD radix sort
String[] tempstrs = asciis;
String[] result = new String[asciis.length];
int[] indexes = new int[256];
for (String str : tempstrs) {
if (str.length() - 1 < index) {
indexes[0]++;
}
else {
char ch = str.charAt(index);
indexes[(int) ch]++;
}
}
int pos = 0;
int[] starts = new int[256];
for (int i = 0; i < indexes.length; i += 1) {
starts[i] = pos;
pos += indexes[i];
}
for (String str:tempstrs) {
if (str.length() -1 < index) {
int place = starts[0];
result[place] = str;
starts[0] += 1;
}
else {
int place = starts[str.charAt(index)];
result[place] = str;
starts[str.charAt(index)] += 1;
}
}
return result;
} SeamCarver
public double energy(int x, int y) {
if (x<0 || x>= width() || y< 0 || y>= height()) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
int lft = x-1 < 0 ? width()-1 : x-1;
int rht = x+1 >= width() ? 0 : x+1;
int up = y-1 < 0 ? height()-1 : y-1;
int down = y+1 >= height() ? 0 : y+1;
Picture pic =this.picture();
double detx = Math.pow((pic.get(rht,y).getRed()-pic.get(lft,y).getRed()),2) +Math.pow((pic.get(rht,y).getBlue()-pic.get(lft,y).getBlue()),2)
+Math.pow((pic.get(rht,y).getGreen()-pic.get(lft,y).getGreen()),2);
double dety = Math.pow((pic.get(x,up).getRed()-pic.get(x,down).getRed()),2) +Math.pow((pic.get(x,up).getBlue()-pic.get(x,down).getBlue()),2)
+Math.pow((pic.get(x,up).getGreen()-pic.get(x,down).getGreen()),2);
return detx +dety;
}
public int[] findVerticalSeam() {
double[][] en = new double[width()][height()];
int[][] path =new int[width()][height()];
for (int i =0;i<width();i++) {
for (int j= 0;j<height();j++) {
en[i][j] = energy(i,j);
}
}
double[][] M = new double[width()][height()];
for (int i =0;i< width();i++) {
M[i][0] = en[i][0];
}
for (int j = 1;j < height();j++) {
M[0][j] = min(M[1][j-1],M[0][j-1]);
if (M[0][j] == M[1][j-1]) path[0][j] = 1;
else path[0][j]=0;
M[0][j]+=en[0][j];
M[width()-1][j] = min(M[width()-1][j-1],M[width()-2][j-1]);
if (M[width()-1][j] == M[width()-1][j-1]) path[width()-1][j] = 0;
else path[0][j]=-1;
M[width()-1][j]+=en[width()-1][j];
for (int i =1;i<=width()-2;i++) {
M[i][j] = min(min(M[i-1][j-1],M[i][j-1]),M[i+1][j-1]);
if (M[i][j] == M[i-1][j-1]) path[i][j]=-1;
else if (M[i][j] == M[i][j-1]) path[i][j] = 0;
else path[i][j] = 1;
M[i][j]+=en[i][j];
}
}
double min = Double.MAX_VALUE;
int xindex = 0;int yindex = height()-1;
for (int i = 0;i<width();i++){
min = Math.min(min, M[i][height() - 1]);
if (min == M[i][height()-1]) xindex = i;
}
int[] finalpath =new int[height()];
while (yindex>=0) {
finalpath[yindex] = xindex;
xindex+=path[xindex][yindex];
yindex--;
}
return finalpath;
}